Row
A control that displays its children in a horizontal array.
To cause a child control to expand and fill the available horizontal space set its expand property.
Examples
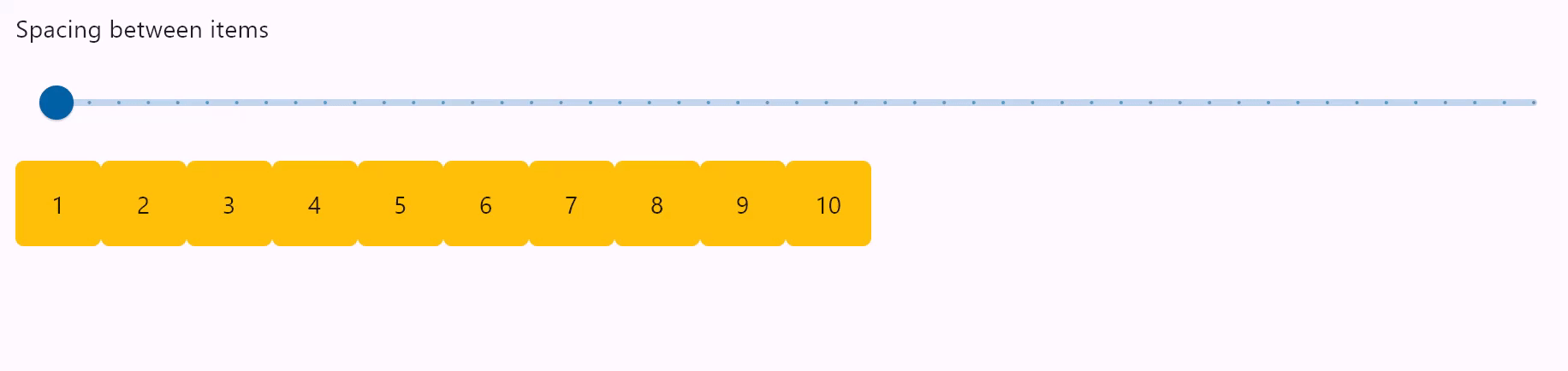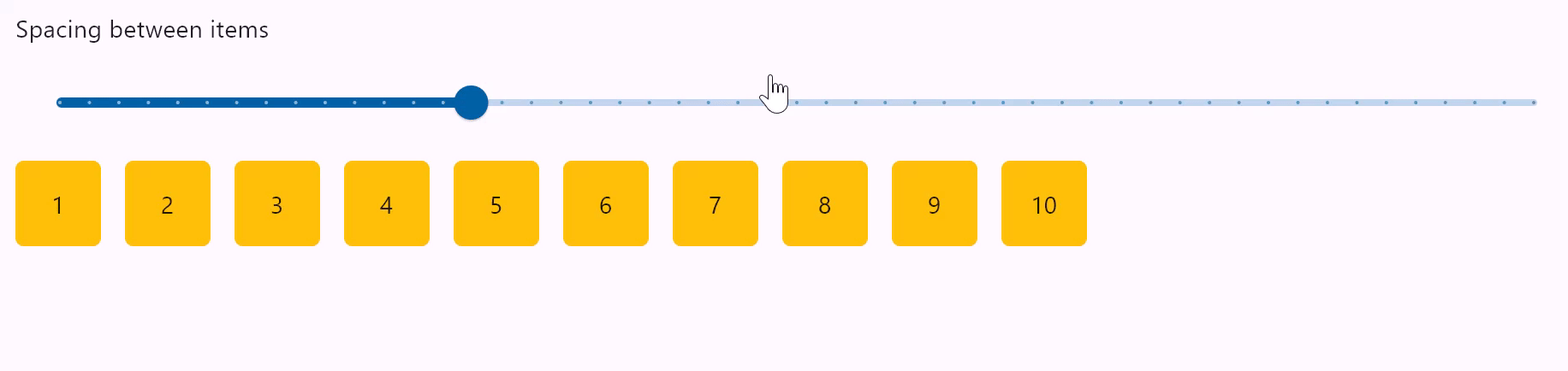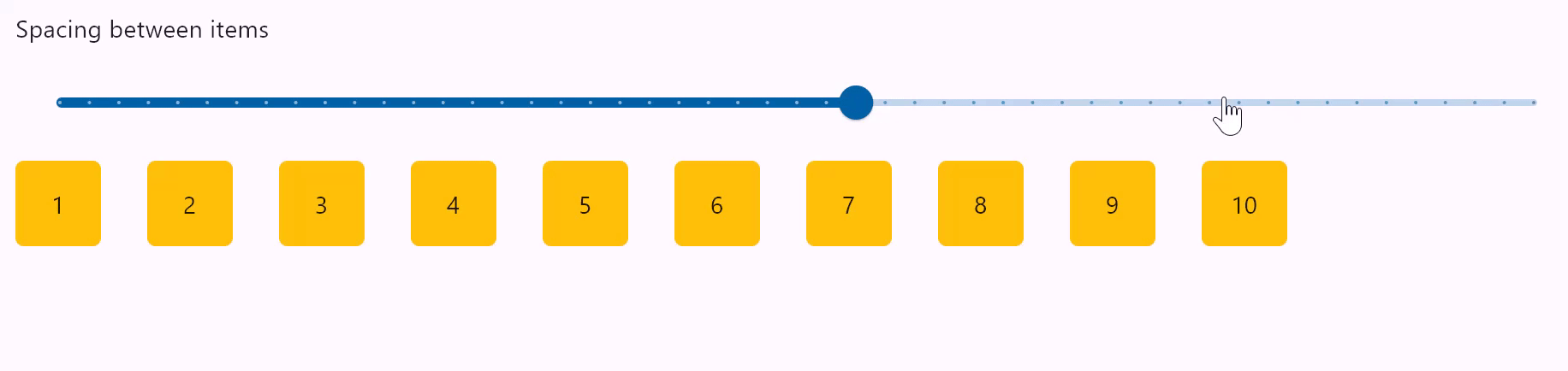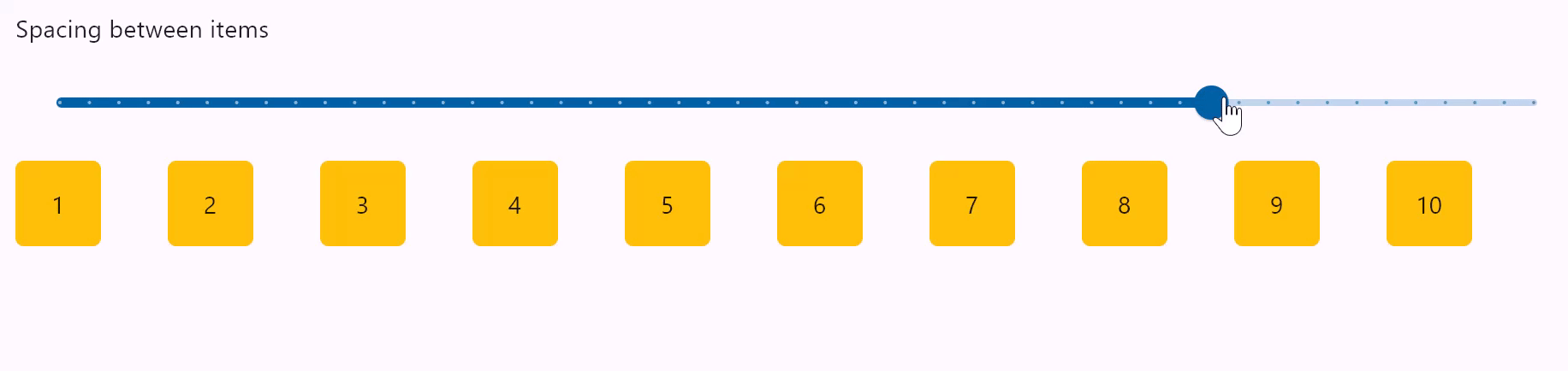
Row spacing
- Python
import flet as ft
def main(page: ft.Page):
def items(count):
items = []
for i in range(1, count + 1):
items.append(
ft.Container(
content=ft.Text(value=str(i)),
alignment=ft.alignment.center,
width=50,
height=50,
bgcolor=ft.colors.AMBER,
border_radius=ft.border_radius.all(5),
)
)
return items
def gap_slider_change(e):
row.spacing = int(e.control.value)
row.update()
gap_slider = ft.Slider(
min=0,
max=50,
divisions=50,
value=0,
label="{value}",
on_change=gap_slider_change,
)
row = ft.Row(spacing=0, controls=items(10))
page.add(ft.Column([ ft.Text("Spacing between items"), gap_slider]), row)
ft.app(target=main)
Row wrapping
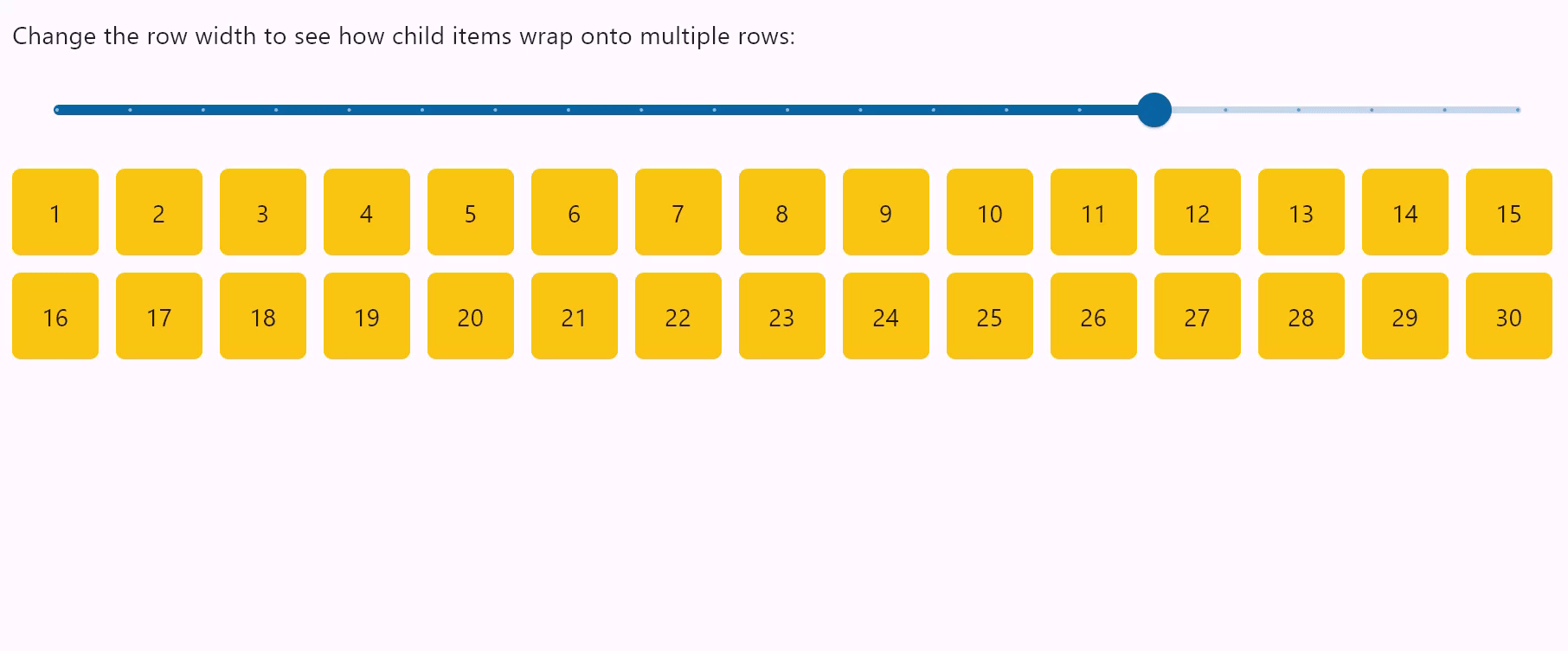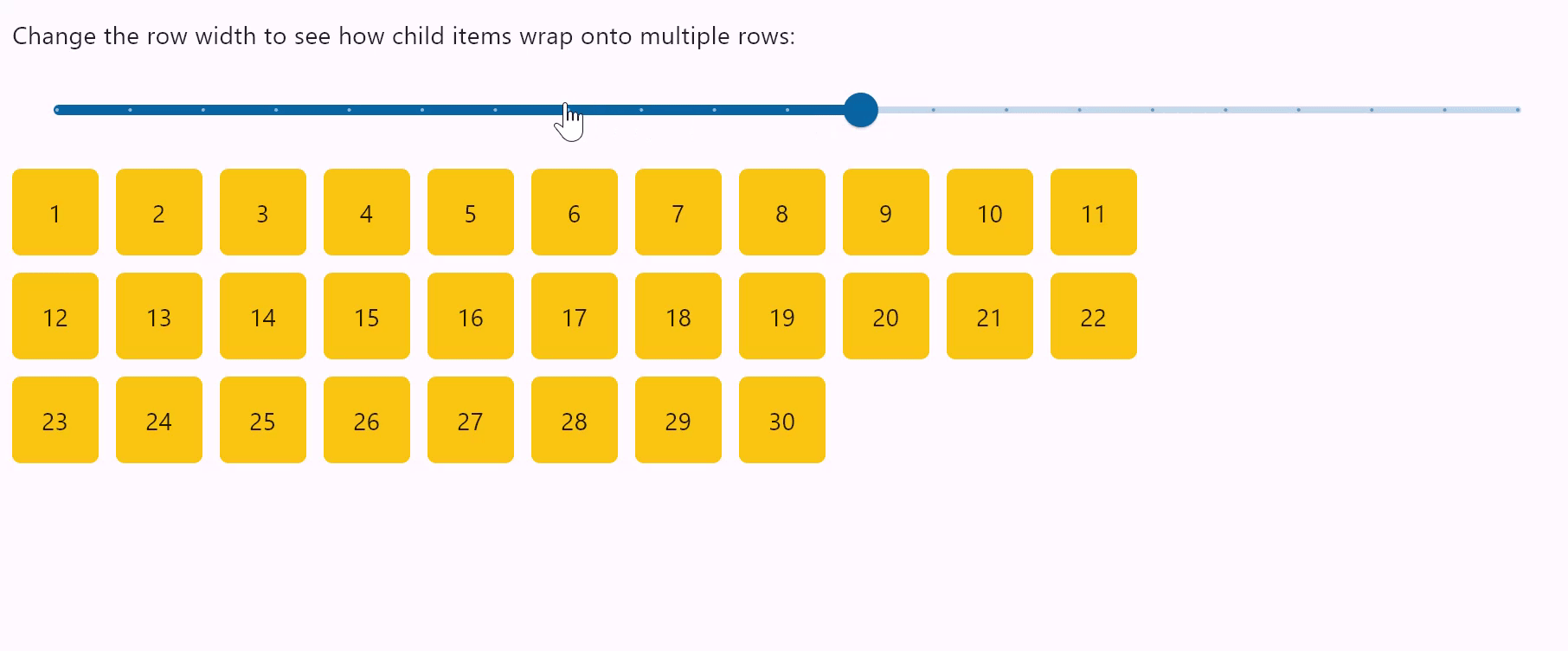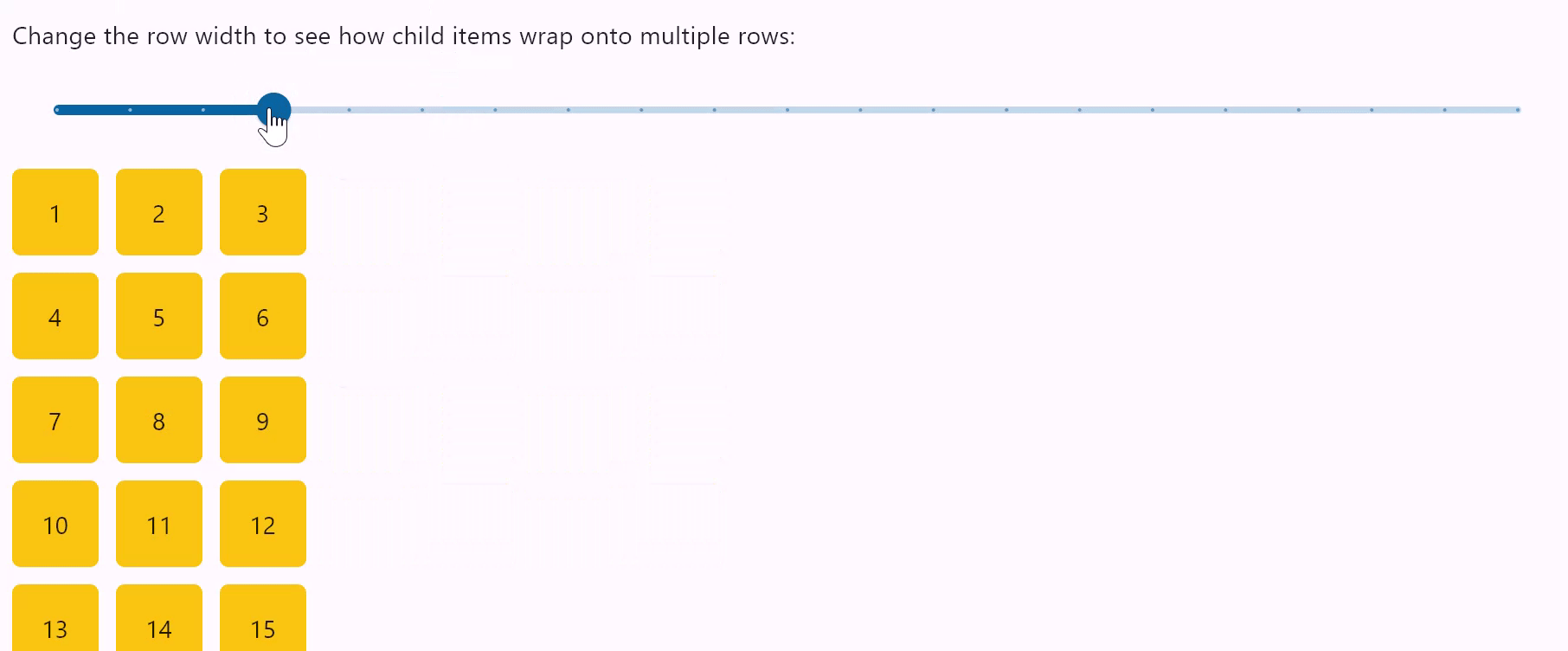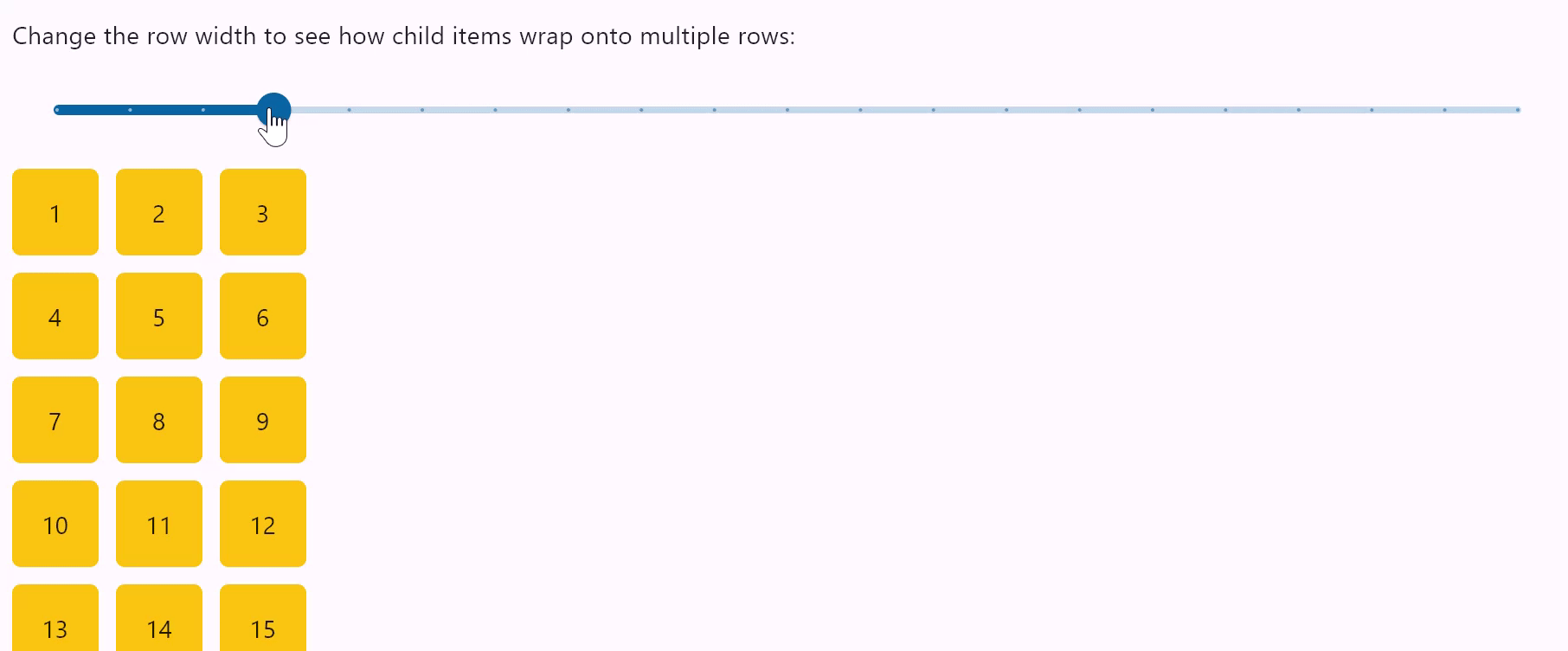
- Python
import flet as ft
def main(page: ft.Page):
def items(count):
items = []
for i in range(1, count + 1):
items.append(
ft.Container(
content=ft.Text(value=str(i)),
alignment=ft.alignment.center,
width=50,
height=50,
bgcolor=ft.colors.AMBER,
border_radius=ft.border_radius.all(5),
)
)
return items
def slider_change(e):
row.width = float(e.control.value)
row.update()
width_slider = ft.Slider(
min=0,
max=page.window_width,
divisions=20,
value=page.window_width,
label="{value}",
on_change=slider_change,
)
row = ft.Row(
wrap=True,
spacing=10,
run_spacing=10,
controls=items(30),
width=page.window_width,
)
page.add(
ft.Column(
[
ft.Text(
"Change the row width to see how child items wrap onto multiple rows:"
),
width_slider,
]
),
row,
)
ft.app(target=main)
Row horizontal alignments
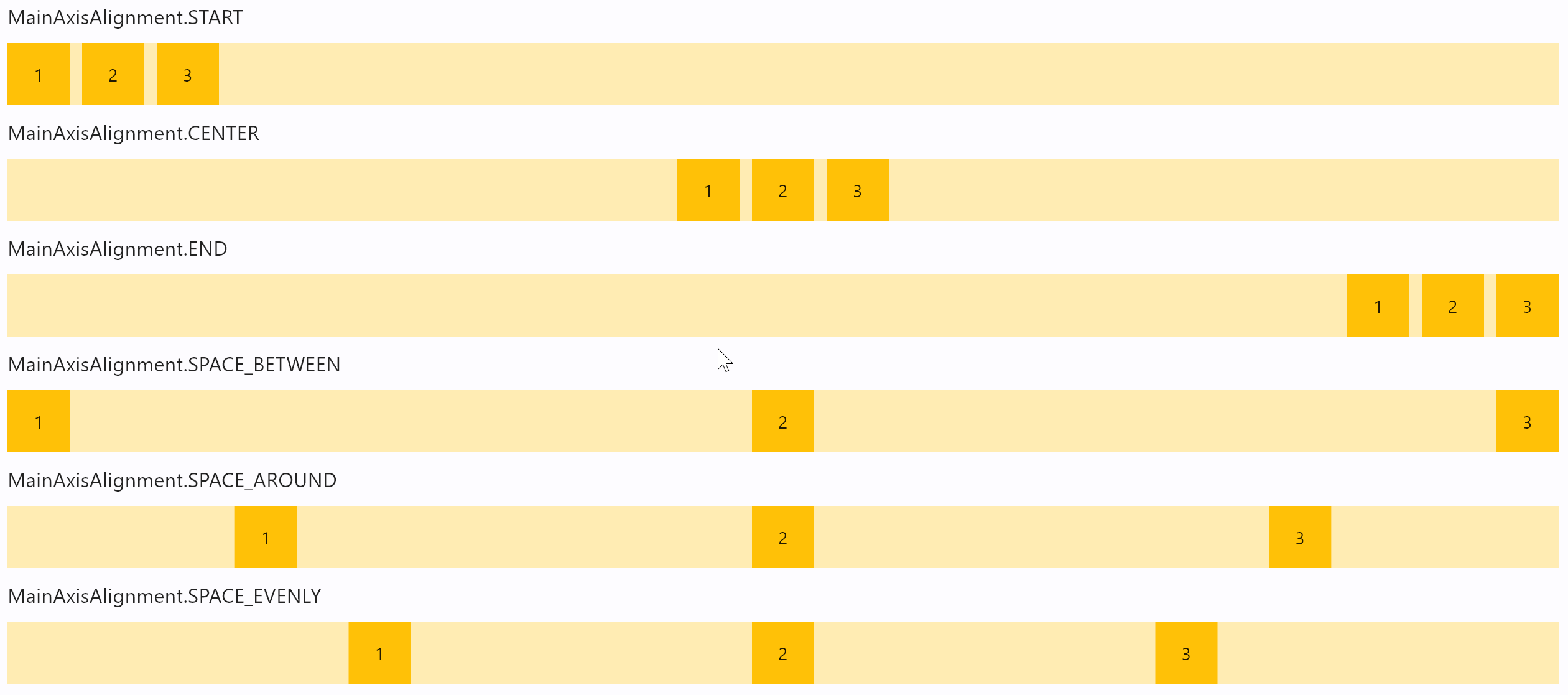
- Python
import flet as ft
def main(page: ft.Page):
def items(count):
items = []
for i in range(1, count + 1):
items.append(
ft.Container(
content=ft.Text(value=str(i)),
alignment=ft.alignment.center,
width=50,
height=50,
bgcolor=ft.colors.AMBER_500,
)
)
return items
def row_with_alignment(align: ft.MainAxisAlignment):
return ft.Column(
[
ft.Text(str(align), size=16),
ft.Container(
content=ft.Row(items(3), alignment=align),
bgcolor=ft.colors.AMBER_100,
),
]
)
page.add(
row_with_alignment(ft.MainAxisAlignment.START),
row_with_alignment(ft.MainAxisAlignment.CENTER),
row_with_alignment(ft.MainAxisAlignment.END),
row_with_alignment(ft.MainAxisAlignment.SPACE_BETWEEN),
row_with_alignment(ft.MainAxisAlignment.SPACE_AROUND),
row_with_alignment(ft.MainAxisAlignment.SPACE_EVENLY),
)
ft.app(target=main)
Row vertical
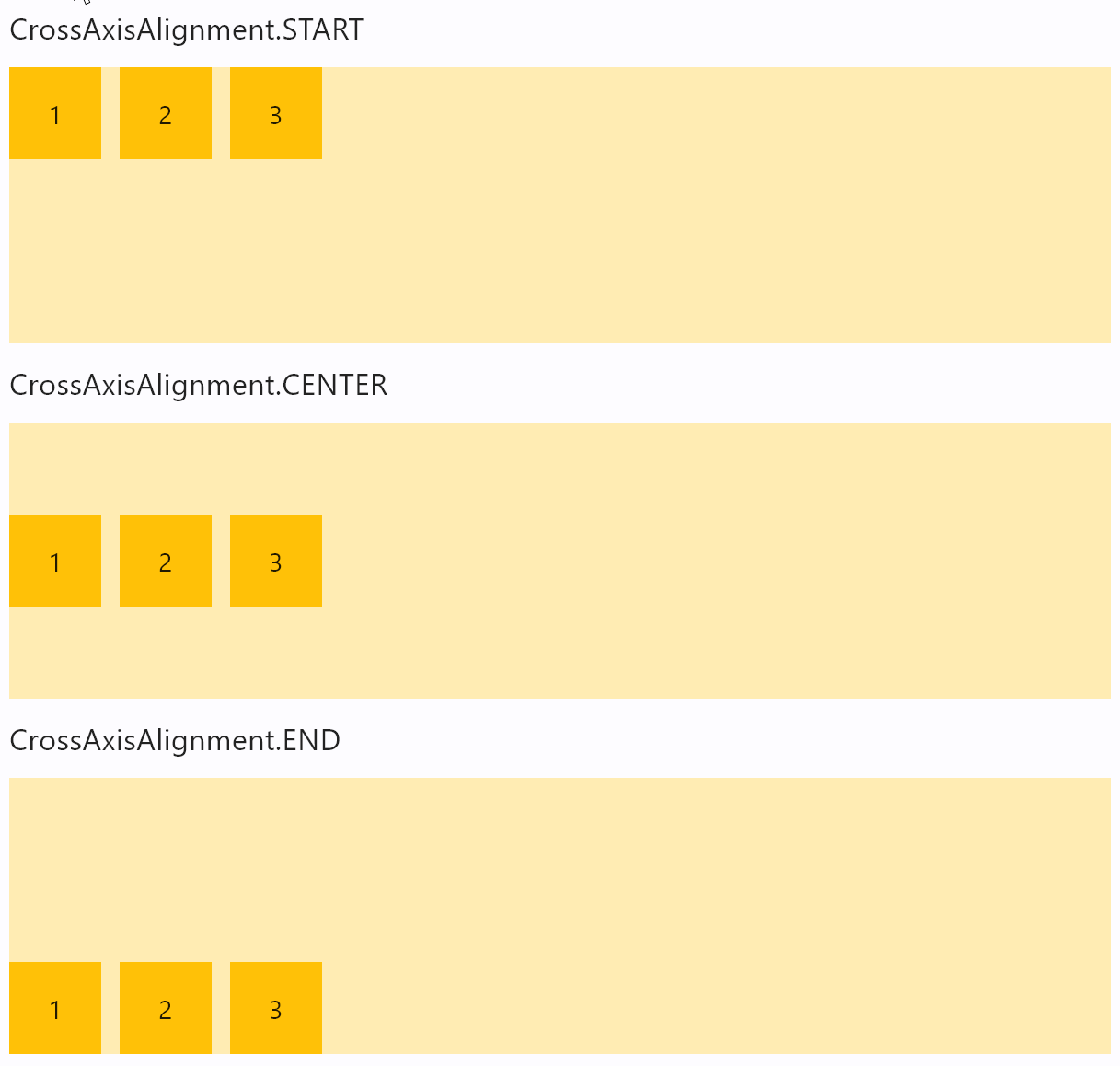
- Python
import flet as ft
def main(page: ft.Page):
def items(count):
items = []
for i in range(1, count + 1):
items.append(
ft.Container(
content=ft.Text(value=str(i)),
alignment=ft.alignment.center,
width=50,
height=50,
bgcolor=ft.colors.AMBER_500,
)
)
return items
def row_with_vertical_alignment(align: ft.CrossAxisAlignment):
return ft.Column(
[
ft.Text(str(align), size=16),
ft.Container(
content=ft.Row(items(3), vertical_alignment=align),
bgcolor=ft.colors.AMBER_100,
height=150,
),
]
)
page.add(
row_with_vertical_alignment(ft.CrossAxisAlignment.START),
row_with_vertical_alignment(ft.CrossAxisAlignment.CENTER),
row_with_vertical_alignment(ft.CrossAxisAlignment.END),
)
ft.app(target=main)
Properties
alignment
How the child Controls should be placed horizontally.
For example, MainAxisAlignment.START, the default, places the children on the left of a Row.
Property value is MainAxisAlignment enum with the following values:
START(default)ENDCENTERSPACE_BETWEENSPACE_AROUNDSPACE_EVENLY
auto_scroll
True if scrollbar should automatically move its position to the end when children updated. Must be False for scroll_to() method to work.
controls
A list of Controls to display inside the Row.
run_spacing
Spacing between runs when wrap=True. Default value is 10.
scroll
Enables horizontal scrolling for the Row to prevent its content overflow.
Property value is an optional ScrollMode enum with None as default.
Supported values:
None(default) - the Row is non-scrollable and its content could overflow.AUTO- scrolling is enabled and scroll bar is only shown when scrolling occurs.ADAPTIVE- scrolling is enabled and scroll bar is always shown when running app as web or desktop.ALWAYS- scrolling is enabled and scroll bar is always shown.HIDDEN- scrolling is enabled, but scroll bar is always hidden.
spacing
Spacing between controls in a row. Default value is 10 virtual pixels. Spacing is applied only when alignment is set to start, end or center.
on_scroll_interval
Throttling in milliseconds for on_scroll event. Default is 10.
tight
Specifies how much space should be occupied horizontally. Default is False - allocate all space to children.
vertical_alignment
How the child Controls should be placed vertically.
Property value is CrossAxisAlignment enum with the following values:
START(default)CENTERENDSTRETCHBASELINE
wrap
When set to True the Row will put child controls into additional rows (runs) if they don't fit a single row.
on_scroll
Fires when row's scroll position is changed by a user.
See Column.on_scroll for event details and examples.
Methods
scroll_to(offset, delta, key, duration, curve)
Moves scroll position to either absolute offset, relative delta or jump to the control with specified key.
See Column.scroll_to() for method details and examples.
Events
on_scroll
Fires when scroll position is changed by a user.
See Column.on_scroll for event details and examples.
Expanding children
When a child Control is placed into a Row you can "expand" it to fill the available space. Every Control has expand property that can have either a boolean value (True - expand control to fill all available space) or an integer - an "expand factor" specifying how to divide a free space with other expanded child controls. For example, this code creates a row with a TextField taking all available space and an ElevatedButton next to it:
r = ft.Row([
ft.TextField(hint_text="Enter your name", expand=True),
ft.ElevatedButton(text="Join chat")
])
The following example with numeric expand factors creates a Row with 3 containers in it and having widths of 20% (1/5), 60% (3/5) and 20% (1/5) respectively:
r = ft.Row([
ft.Container(expand=1, content=ft.Text("A")),
ft.Container(expand=3, content=ft.Text("B")),
ft.Container(expand=1, content=ft.Text("C"))
])
In general, the resulting width of a child in percents is calculated as expand / sum(all expands) * 100%.